Your Branched Scenario Needs to Look Like Something. Is this it?
October 30th, 2018
Developing the content and flow of an interactive branched scenarios is one thing. Creating the visual structure is another. In today’s post we’ll look at some key considerations when building scenarios and come up with a simple storyboarding process to help think through the scenario design and layouts.
Branched Scenarios: 3C Model
Years ago, I introduced the 3C model to build interactive scenarios: challenge, choices, and consequences. It’s a simple model to help think through the content requirements. It starts with challenging the learner’s understanding through some sort of contextual and real-world situation where decisions need to be made. Give them some choices to make. And the choices produce consequences.
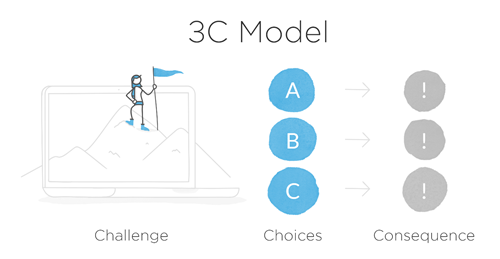
The consequences can be simple with immediate feedback or the 3C model can be compounded where each consequence produces another challenge and branches indefinitely. Of course, it’s hard enough to get your subject matter expert to give you ten good multiple-choice questions, let alone provide all of the content and nuance to build a complex branched interaction. I prefer a simple scenario structure.
Branched Scenarios: Visual Structure
A branched scenario starts with a blank screen. And from there, we add the scenario structure. But what exactly is it that we need and how do we design the screen layouts?
Let’s start with what needs to be on the screen. Here are a few of the main onscreen components that make up many branched scenarios:
- Background: the background (or environment) is an easy way to establish context. I usually look for a single image that helps do that.
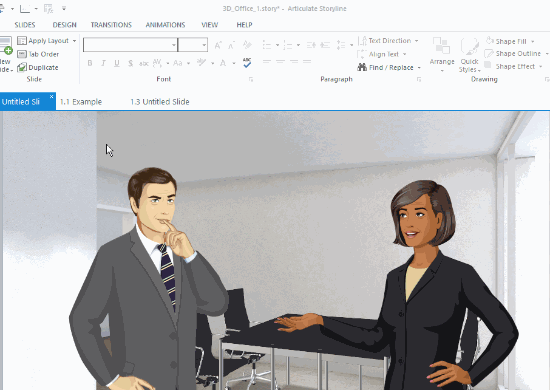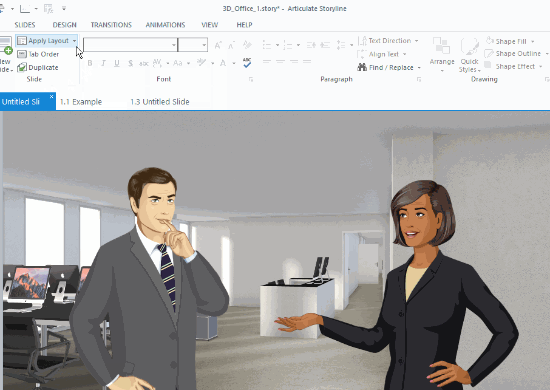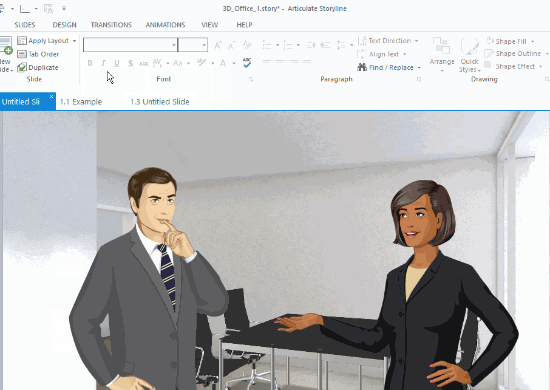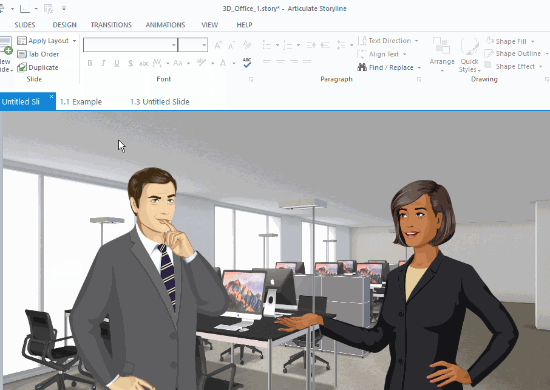
- Characters: generally speaking there are actors in the scenario. Sometimes they can be implied and don’t need to be onscreen. For example, looking at an email or text message implies that someone in the scenario is viewing it. Or perhaps, the learner is the character. However, in many cases, the scenario actually features characters. Is it one or more? How do you show back and forth conversation?
- Challenge: the screen consists of some text that presents the situation and challenge. That text needs to go somewhere. Does it go up, down, left or right? Is it there to start, or does it get exposed when the user does something like click a button?
- Choices: once the challenge is presented, the learner has to make a decision. That usually means there’s an assortment of choices and then some sort of button (or other interaction) to make the selection. Where will that be on the screen?
- Consequences: each choice usually includes some sort of feedback. It could be all of the feedback or perhaps an alert that the decision has created a new challenge. In either case, how is that displayed?
Branched Scenario: Simplify with a Storyboard
As you review the list above, it becomes apparent that there’s a lot to put on the screen. In workshops we usually create a blank slide and then a box to represent all of those things above. Then we play around with layouts to see what we can get onscreen. After that, we explore different ways to move the content offscreen and use triggered actions to expose the content.
There’s a lot that makes up the scenario layout. The image below represents some common scenario layouts.

Of course, there are all sorts of ways to structure a scenario. Keep in mind not everything needs to go on one screen. You can use layers and lightboxes to expose additional content. Mouseover interactions are great to expand information without requiring that the person leave the current screen.
One way to get started is to create three blank slides: one for each part of the 3C model.
- Challenge slide: set up the scenario by adding visual context and all the supporting text. You’re not writing War and Peace. Keep it short and get right to the point.
- Choice slide: determine how many choices the person will have. Also determine if you will present ancillary options. For example, you may want some links to talk to team members or contact HR for more assistance. What will those look like, where will they be placed on the screen, and what does the content look like?
- Consequence slide: what feedback needs to be displayed? Is it just text? Will there be a character?

Once you have the three elements on separate slides, it’s easier to see what you have to expose during the scenario. From there you can begin to assemble the screen. Some people create cheats. For example, create a “folder” that can be placed on a different slide or layer. The folder is a good metaphor and fits a lot of contexts. It’s also a nice visual that can hold a lot of content. It allows you to get rid of character images, buttons and a lot of the other clutter that you have using a single slide.
In a previous post, I simplified the process by suggesting that you use a visual container. The container adds context and holds the text. That’s one option. But there are a lot more. The key is to determine what you need first using the three slides. And then from there play around with ideas on what to add to the screen and what to expose later and when to expose it.
Events
- Everyday. Check out the weekly training webinars to learn more about Rise, Storyline, and instructional design.
Free E-Learning Resources
 |
 |
 |
|
Want to learn more? Check out these articles and free resources in the community. |
Here’s a great job board for e-learning, instructional design, and training jobs |
Participate in the weekly e-learning challenges to sharpen your skills |
 |
 |
 |
|
Get your free PowerPoint templates and free graphics & stock images. |
Lots of cool e-learning examples to check out and find inspiration. |
Getting Started? This e-learning 101 series and the free e-books will help. |