The Power of Functional Prototypes for E-Learning
October 24th, 2017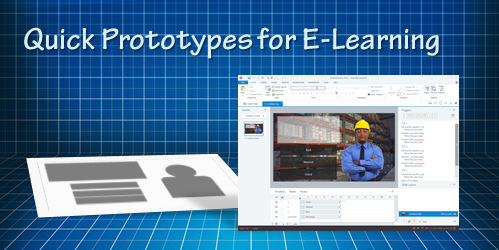
Many e-learning developers spend too much time building courses that are almost complete before they solicit feedback about the course. This could be a waste of resources because by that time, they’ve invested a lot of resources and it’s a real challenge to get things changed that late in the game, especially if the changes are significant.
A better solution is to quickly prototype the course, get some feedback and make adjustments. This is even more critical if you have a lot of interactive content. The good thing is that this is really easy to do in Storyline (or event PowerPoint).
Here are a few tips on how to approach the prototyping.
E-Learning Prototype: Start Backwards
What is the objective of the course and what does the client expect the learner to do? Slapping a bunch of information together over a series of screens is probably not going to meet your objectives.
It’s all about the action, boss.
It doesn’t take much effort to prototype a bullet point screen. That’s not where you want to put your effort when you prototype. Instead, focus on the actions and prototype the activities that let the learners practice and demonstrate understanding.
What do they need to do and what interaction can you build that allows them to do that?
E-Learning Prototype: Build Something that Works
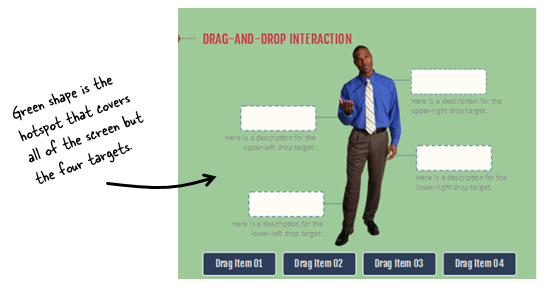
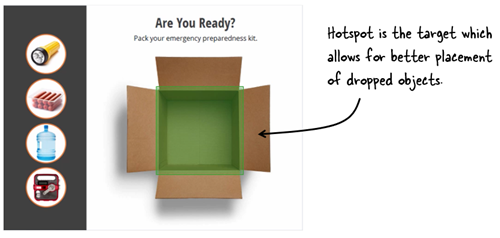
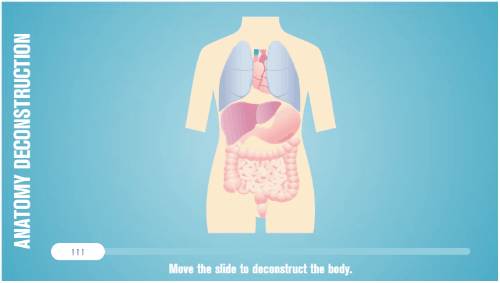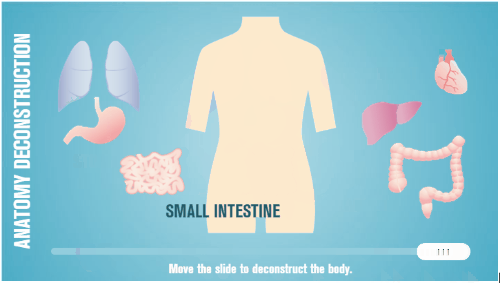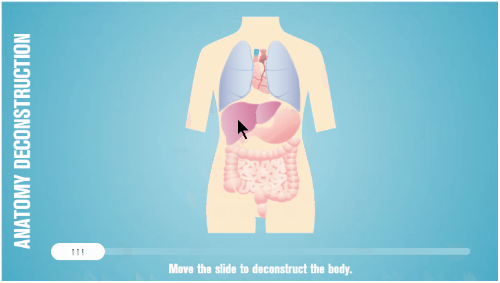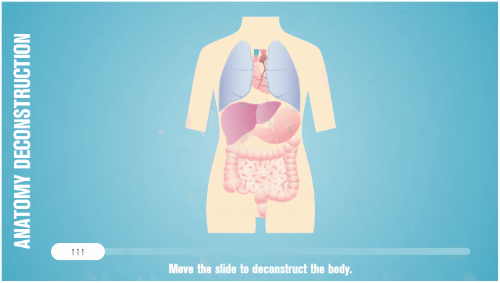
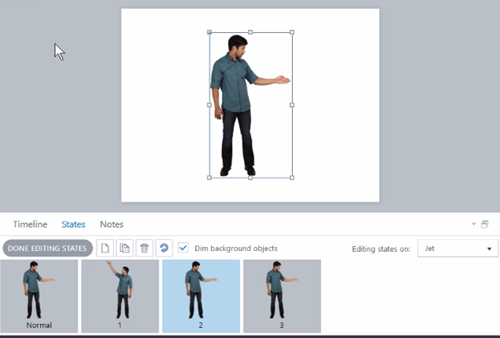
One of the many things I like about Storyline is how easy it is to prototype all sorts of interactions. In fact, someone told me that she was in a meeting with a potential client who shared their course requirements and what they hoped to get out of the course.
While the potential client was talking, the e-learning developer opened Storyline and built a quick mock-up of how the course could work with some simple interactions and decision-making scenarios. The client intended to send her away to build something to pitch later. Instead, the e-learning developer showed her the interactive prototype right there in the meeting and got the job on the spot. All because she was able to focus on the desired activity and build a working model.
E-Learning Prototype: Don’t Worry About Looks
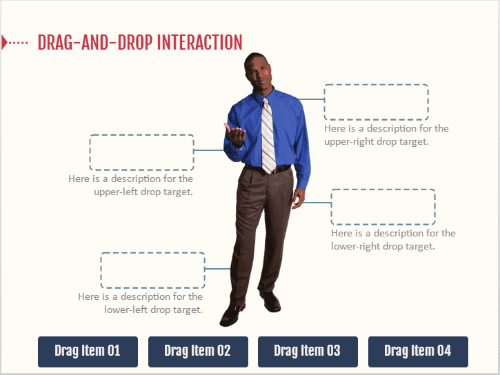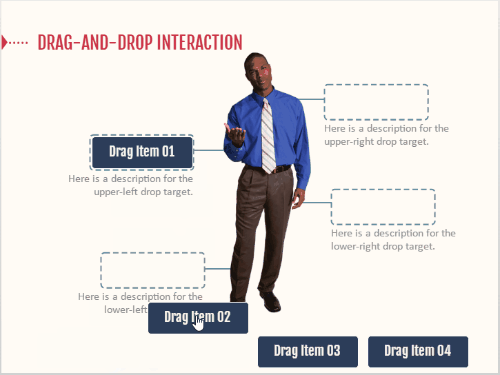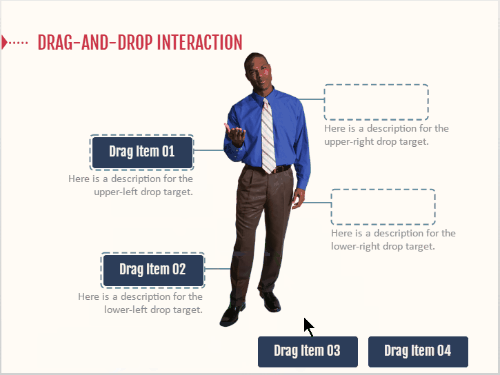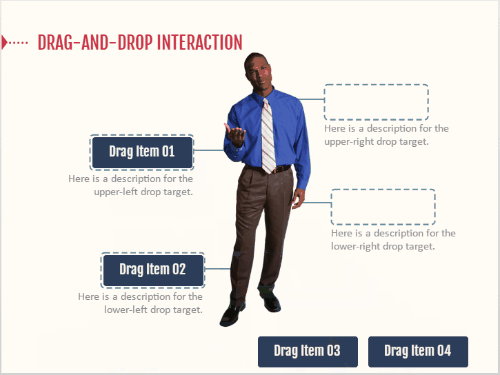
At our workshops, we like to present a few challenge activities. This lets people workout ideas and build quick interactive modules. However, there are always a few attendees who end up spending all their time on the visual design and never end up building a working interactive prototype.
It’s an easy trap to fall into because we tend to lean on the visuals first. They help us think about the project. However, it’s a trap that wastes time. Don’t worry about the way the module looks, worry about the functionality and the desired output.
Of course, you do want it to be visually organized. If not, the customer will still focus on the way it looks. But you don’t need to make it visually rich. A good cheat though, is to start with the content library templates and then work from there.
To sum it all up, building quick prototypes is a better option for course development than building almost complete courses and then soliciting feedback, especially since you’ll probably have to make a bunch of changes anyway.
How do you build your prototypes? Do you start with a storyboard? Or do you jump right into the software and start building?
Events
- Everyday. Check out the weekly training webinars to learn more about Rise, Storyline, and instructional design.
Free E-Learning Resources
 |
 |
 |
|
Want to learn more? Check out these articles and free resources in the community. |
Here’s a great job board for e-learning, instructional design, and training jobs |
Participate in the weekly e-learning challenges to sharpen your skills |
 |
 |
 |
|
Get your free PowerPoint templates and free graphics & stock images. |
Lots of cool e-learning examples to check out and find inspiration. |
Getting Started? This e-learning 101 series and the free e-books will help. |



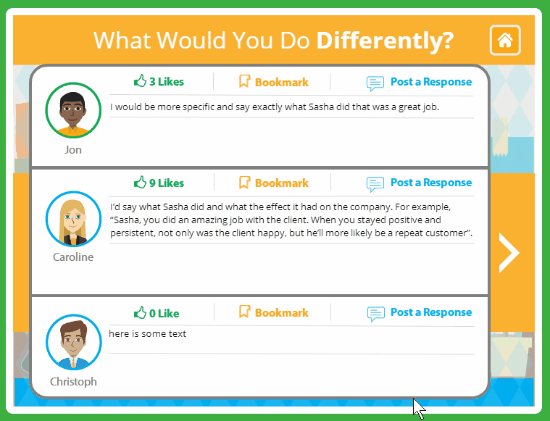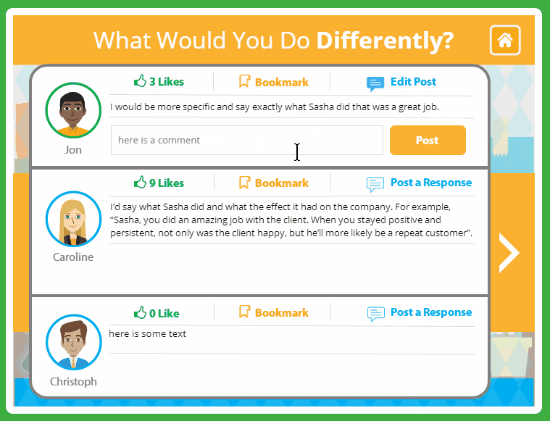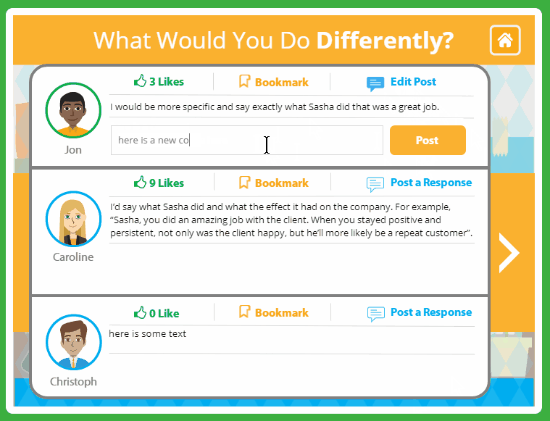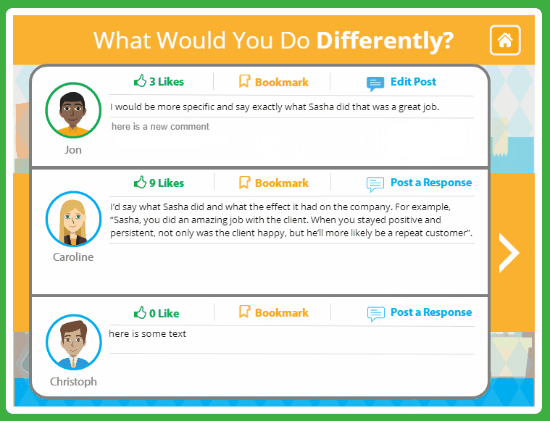
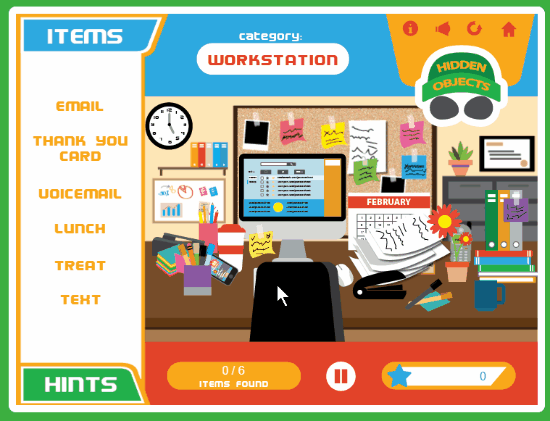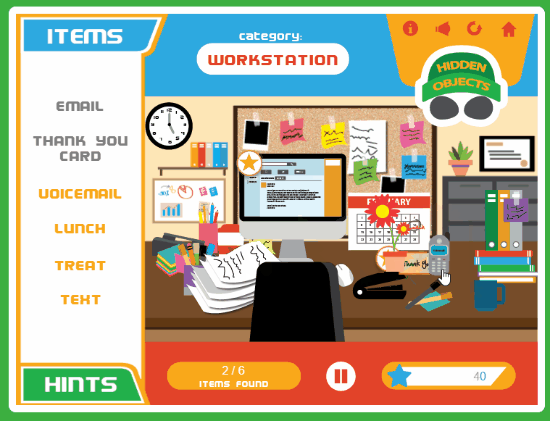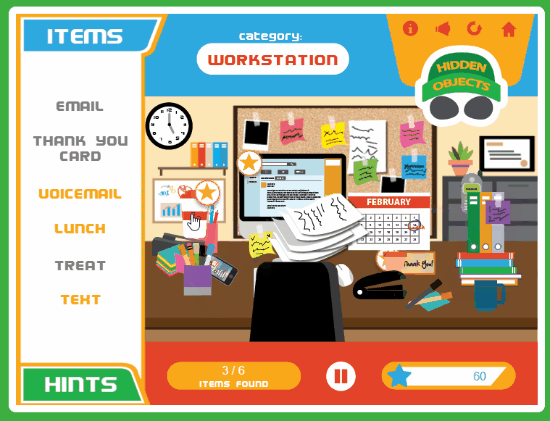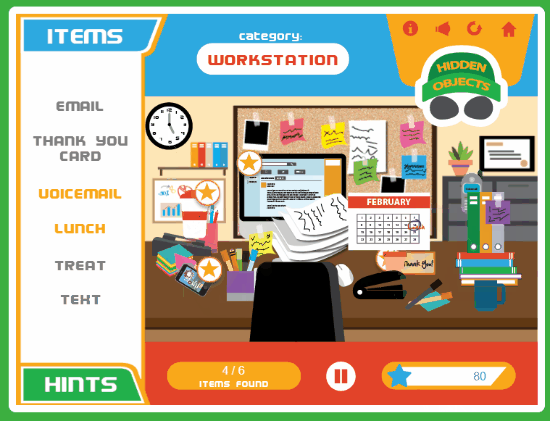



















3
comments